
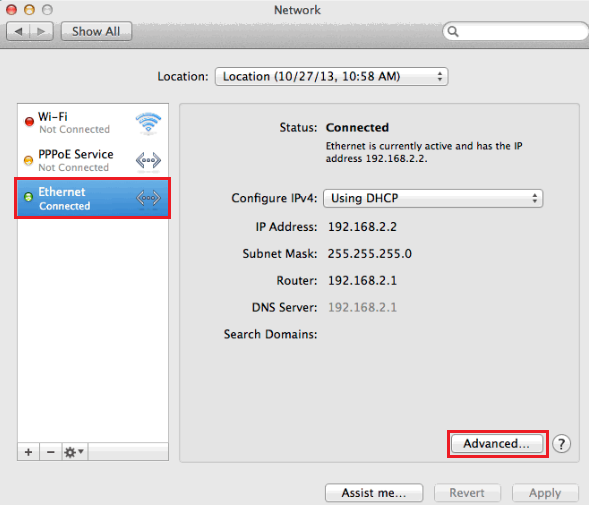
In many ways, a DNS server is similar to the once-commonplace telephone directory service, where you only need to remember a person’s name and not their phone number. This page appears on your screen right now because such a process has worked. This process is necessary because computers only understand numbers while humans are pretty bad at remembering them. The browser then follows that IP address to load the website.
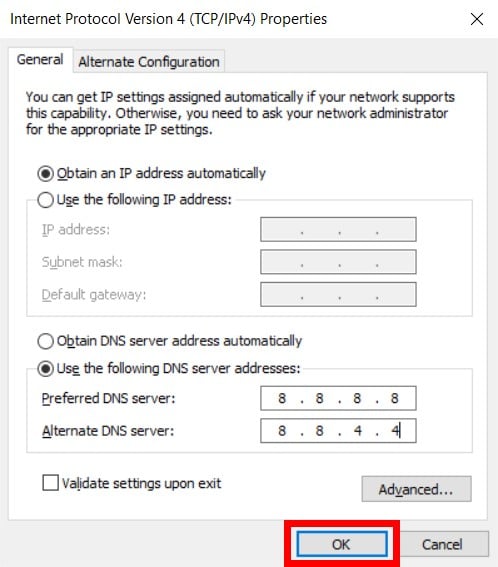
web address or URL) and returns its IP address, which is a string of seemingly random numbers, to the browser - each website resides at an IP address. This server then looks up the website’s domain name (a.k.a. By default, that’s the server of the Internet provider. Whenever you access a website via its domain name, such as, the browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.) first queries your DNS server.įor most homes, the Wi-Fi router holds the information of the DNS server in use. Here’s a typical example of the role DNS plays: (A DNS server is not to be confused with Dynamic DNS, which works somewhat the opposite way.) Steps to change DNS settings in a Windows computerĭomain Name System Explained: What it is and how a DNS server worksĪ DNS server is like a public directory of the Internet.How to change DNS settings to better your Internet.DNS is a matter of privacy and control, too.Domain Name System Explained: What it is and how a DNS server works.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
